APCCAS 2024
log mel-spectrogram implementation
A 250.3mW Versatile Sound Feature Extractor Using 1024-Point FFT 64-ch LogMel Filter in 40nm CMOS
Akiho Kawada*, Kenji Kobayashi*, Jaewon Shin, Rei Sumikawa, Mototsugu Hamada, Atsutake Kosuge
* Equal contribution
Abstract
A 250.3µW always-on sound feature extractor that facilitates general-purpose sound recognition AI processing encompassing 35-word voice command recognition, environmental sound recognition, and musical instrument recognition is developed.
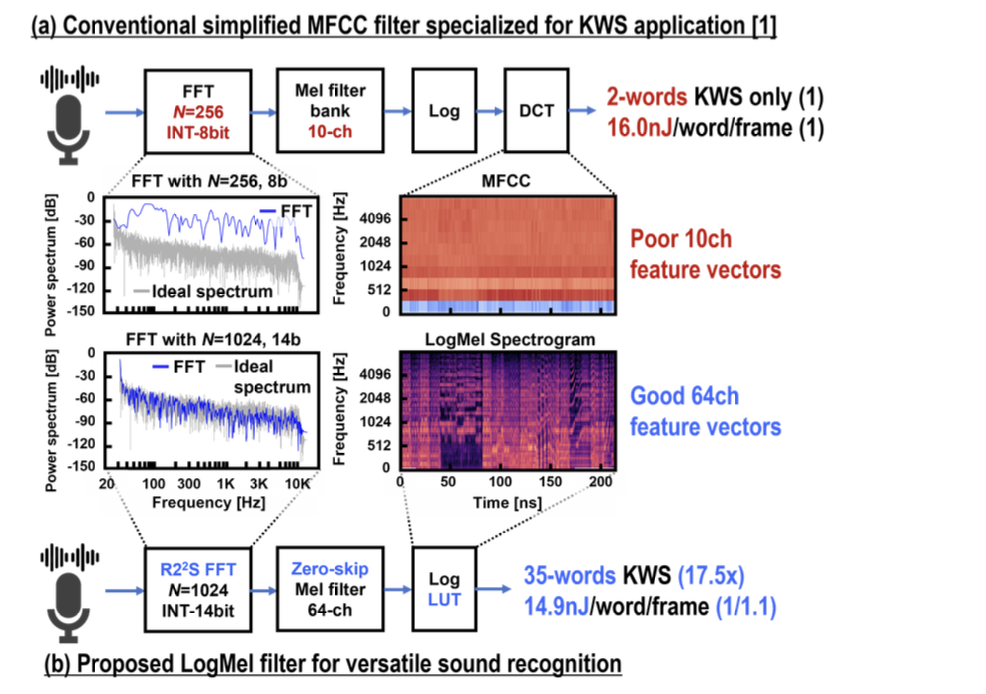
Conventionally, approximated mel- frequency cepstrum coefficients (MFCC) feature extractors composed of a limited number of FFT samples (256 points), and filter channels (10 channels) are utilized for energy reduction; however, their applicability is restricted to wake-up word recognition resulting in high NRE costs.
To overcome these challenges, we developed a LogMel filter feature extractor employing a 1024-point FFT and 64-channel Mel filter bank, which enables versatile applications across a diverse range of sound recognition tasks including 35-word voice command recognition. To minimize circuit area and power consumption, three techniques are employed:
(a) radix-22 single-path delay feedback (R22SDF) which uses serial FFT processing for circuit area reduction,
(b) zero-skipping Mel filter bank for a 1/25x circuit area reduction by storing and accumulating only non- zero elements, and
(c) Log LUT, an LUT approximation to reduce the number of cycles by a factor of 20 compared with the CORDIC implementation.
Designed and implemented in a 40nm CMOS process, the proposed extractor demonstrates a power efficiency of 14.9nJ/frame/word for a 35-word voice command recognition task, showcasing a 1.1× improvement in power efficiency and a 17.5 × increase in the number of recognizable voice commands compared to state-of-the-art KWS-specific simplified MFCC audio extraction circuits.